A new empirical formulation for the out-of-plane resistance of infilled reinforced concrete frames without prior in-plane loading
Abstract
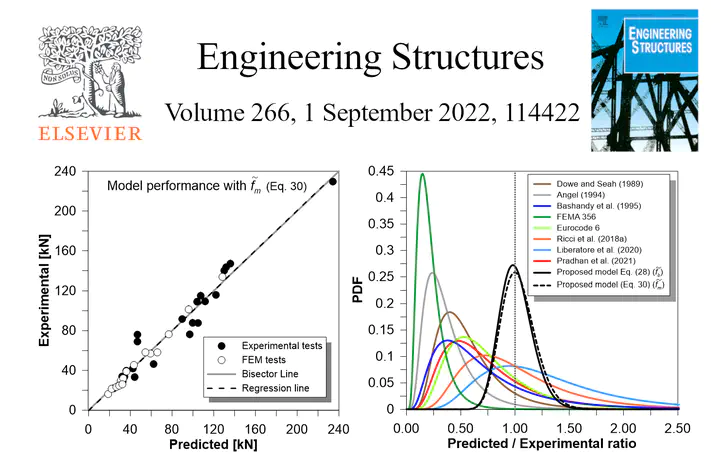
The paper presents a new empirical expression estimating the out-of-plane (OOP) resistance of infilled reinforced concrete frames subject to horizontal forces. The new model is calibrated through an optimization process based on a hybrid dataset, including experimental data from real tests and from numerical simulations obtained from a refined FE micro-model realized in Abaqus. The new expression considers the effect of vertical loads and also introduces a conversion factor to uniformize point-load and uniform load out-of-plane tests. The final expression is also flexible with respect to available data on the infill material properties, as it is specialized in two versions, one providing the conventional compressive strength of the units, the other providing the conventional compressive strength of masonry as possible inputs. Results presented in the paper will show a noticeable accuracy of the proposed model in estimating the ultimate out-of-plane load of a masonry infill wall, with respect to available models. The formula provides a reference undamaged OOP force but can be easily combined with available strength-reduction functions to consider the effect of prior in-plane loading.
Highlights
-
A new empirical formulation for the evaluation of the out-of-plane resistance of masonry infills is presented.
-
The formula is based on a hybrid dataset made of real experimental tests and refined numerical simulations.
-
An in-depth finite element investigation is carried out with a refined micromodel properly validated.
-
The new formula takes into account the effect of vertical loads on the out-of-plane resistance of infills.
-
A conversion factor is introduced to compare point-load and distributed load out-of-plane tests.
-
A comparison with literature models confirms large improvement of predictive capacity by the proposed model.